Step 1: Figure out how long it would take you to sit down and count out the possible values of your variable. For example, if your variable is “Temperature in Arizona,” how long would it take you to write every possible temperature? It would take you literally forever: 50°, 50.1°, 50.11°, 50.111°, 50.1111°, …
Probability Distribution Graphs | Discrete & Continuous – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
1. pound container. The number of applicants for a job. Classify each random variable as either discrete or continuous. The time between customers entering a checkout lane at a retail store. The weight of refuse on a truck arriving at a landfill. The number of passengers in a passenger vehicle on a highway at rush hour.

Source Image: qualaroo.com
Download Image
Mar 12, 202324. State whether the variable is discrete or continuous. A person’s weight. The height of a building. A person’s age. The number of floors of a skyscraper. The number of clothing items available for purchase. 25. State whether the variable is discrete or continuous. Temperature in degrees Celsius. The number of cars for sale at a car

Source Image: toppers4u.com
Download Image
Quantitative vs Qualitative Variable quantitative discrete (5) The number of bread rolls bought each week by a family. quantitative discrete (6) the pets owned by students in your class. Categorical (7) the number of leaves on a rose plant stem. quantitative discrete (8) the number of hours of daylight each day in winter. quantitative continuous

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Determine Whether The Quantitative Variable Is Discrete
quantitative discrete (5) The number of bread rolls bought each week by a family. quantitative discrete (6) the pets owned by students in your class. Categorical (7) the number of leaves on a rose plant stem. quantitative discrete (8) the number of hours of daylight each day in winter. quantitative continuous Determine whether the variable given is qualitative, quantitative–discrete, or quantitative-continuous. allergen level (low/medium/high) quantitative-continuous since this variable would yield numbers that count. quantitative–discrete since this variable would yield numbers that count. qualitative since this variable would yield categories.
Determine whether the variable is qualitative or quantitative. Explain your reasoning. – YouTube
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables: Discrete variables represent counts (e.g. the number of objects in a collection). Continuous variables represent measurable amounts (e.g. water volume or weight). Frequently asked questions: Methodology What is differential attrition? Determine whether the variable is qualitative or quantitative Breed of dog Is | Course Hero

Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
Categorical vs. Quantitative Data: The Difference + Why They’re Valuable | FullStory Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables: Discrete variables represent counts (e.g. the number of objects in a collection). Continuous variables represent measurable amounts (e.g. water volume or weight). Frequently asked questions: Methodology What is differential attrition?

Source Image: fullstory.com
Download Image
Probability Distribution Graphs | Discrete & Continuous – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Step 1: Figure out how long it would take you to sit down and count out the possible values of your variable. For example, if your variable is “Temperature in Arizona,” how long would it take you to write every possible temperature? It would take you literally forever: 50°, 50.1°, 50.11°, 50.111°, 50.1111°, …

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Quantitative vs Qualitative Variable Mar 12, 202324. State whether the variable is discrete or continuous. A person’s weight. The height of a building. A person’s age. The number of floors of a skyscraper. The number of clothing items available for purchase. 25. State whether the variable is discrete or continuous. Temperature in degrees Celsius. The number of cars for sale at a car

Source Image: statisticseasily.com
Download Image
What is Interval Data? Examples & Definitions – Code Institute IE There are two types of quantitative data, which is also referred to as numeric data: continuous and discrete. As a general rule, counts are discrete and measurements are continuous. Discrete data is a count that can’t be made more precise. Typically it involves integers. For instance, the number of children (or adults, or pets) in your family
Source Image: codeinstitute.net
Download Image
Determine whether the variable is qualitative or quantitative Distance in miles | Course Hero quantitative discrete (5) The number of bread rolls bought each week by a family. quantitative discrete (6) the pets owned by students in your class. Categorical (7) the number of leaves on a rose plant stem. quantitative discrete (8) the number of hours of daylight each day in winter. quantitative continuous

Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
Variable types and examples – Stats and R Determine whether the variable given is qualitative, quantitative–discrete, or quantitative-continuous. allergen level (low/medium/high) quantitative-continuous since this variable would yield numbers that count. quantitative–discrete since this variable would yield numbers that count. qualitative since this variable would yield categories.
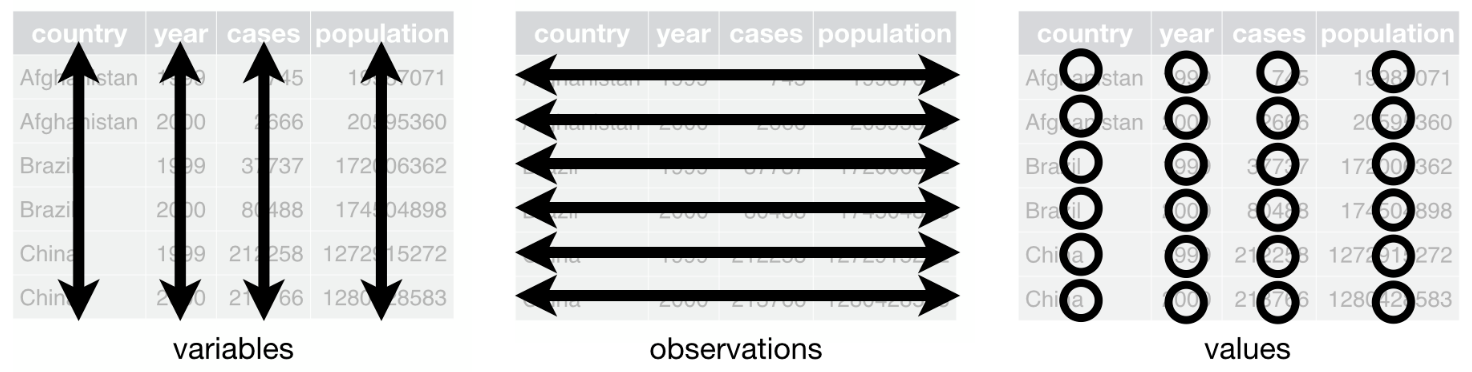
Source Image: statsandr.com
Download Image
Categorical vs. Quantitative Data: The Difference + Why They’re Valuable | FullStory
Variable types and examples – Stats and R 1. pound container. The number of applicants for a job. Classify each random variable as either discrete or continuous. The time between customers entering a checkout lane at a retail store. The weight of refuse on a truck arriving at a landfill. The number of passengers in a passenger vehicle on a highway at rush hour.
Quantitative vs Qualitative Variable Determine whether the variable is qualitative or quantitative Distance in miles | Course Hero There are two types of quantitative data, which is also referred to as numeric data: continuous and discrete. As a general rule, counts are discrete and measurements are continuous. Discrete data is a count that can’t be made more precise. Typically it involves integers. For instance, the number of children (or adults, or pets) in your family